Dockerは、コンテナによりサーバ機能を提供する。コンテナは必要な時に起動し、不要になったら破棄する使い捨ての運用に適している。管理上、通常は1コンテナ1プロセスとして構成する。Dockerは、永続データを保存する用途には適さない。
# 仮想化技術
## ホスト型仮想化
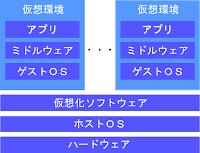
仮想化ソフトをインストールして手軽に仮想環境が構築できるため開発環境の構築などによく使われる。ホストOSの上でゲストOSを動かすので、オーバーヘッドが大きい。
Oracleが提供する「Oracle VM VirtualBox」がある。
## ハイパーバイザー型仮想化
ホストOSがなくハードウェアを直接制御するため、リソースを効率よく使用できる。仮想環境ごとに別のOSが動作するので、仮想環境の起動にかかるオーバーヘッドは大きい。ハイパーバイザー型はファームウェアとして実装されているものが多い。
代表的なものに、Hyper-V、XenServerがある。

## コンテナ型仮想化
ホストOS上に論理的な区画(コンテナ)を作り、アプリケーションを動作させるのに必要なライブラリやアプリケーションなどをコンテナ内に閉じ込め、あたかも個別のサーバのように使うことができるようにしたもの。ホストOSのリソースを論理的に分割し、複数のコンテナで共有して使うため、コンテナ型仮想化はオーバーヘッドが少ない。
Dockerはこれにあたる。

# Dockerが動く仕組み
## コンテナを区画化する仕組み
**コンテナを区画化する仕組み**にLinuxカーネルの**namespace**の機能を使っている。
Linuxカーネルのnamespace機能は、Linuxのオブジェクトに名前を付けることで、次の6つの独立した環境を構築できる。
**PID** namespace
**Network** namespace
**UID** namespace
**MOUNT** namespace
**UTS** namespace
**IPC** namespace
## リソース管理の仕組み
**リソース管理の仕組み**にLinuxカーネルの**cgroup**の機能を使っている。
Linuxカーネルのcgroup機能は、プロセス/スレッドをグループ化して、そのグループ内に存在するプロセス/スレッドに対して、管理を行うための機能。
### cgroupで管理できる主なもの
|項目|説明|
|----|----|
|cpu|CPU使用量の制限|
|cpuacct|CPU使用量の統計情報を提供|
|cpuset|CPUやメモリの配置を制御|
|momory|メモリやスワップの使用量の制限|
|devices|デバイスへのアクセス許可/拒否|
|freezer|グループに属するプロセスの停止/再開|
|net_cls|ネットワーク制御のタグを付加|
|blkio|ブロックデバイスの入出力量制御|
cgroupは、階層構造を使ってプロセスをグループ化して管理する。cgroupの親子関係の間では、子のcgroupは親のcgroupの制限を受ける。

## ネットワーク構成(仮想ブリッジ/仮想NIC)
Dockerのコンテナには、サーバの物理NICとは別にコンテナごとに仮想NICが割り当てられる。これらの仮想NICは**docker0**という仮想ブリッジに接続され、コンテナ同士が通信する。docker0は、Dockerデーモン起動後に作成され、**172.17.42.1**のアドレスが割り当てられる。
Dockerでコンテナを起動すると、コンテナに172.17.0.0.16のサブネットマスクを持つプライベートIPアドレスがeth0に自動的に割り当てられる。コンテナのeth0は、ホストOSに作成された仮想NIC(vethxxx)がペアで割り当てられる。vethはOSI基本参照モデルのレイヤー2の仮想ネットワークインターフェースで、ペアのNIC同士でトンネリング通信を行う。

## Dockerのコンテナ同士の通信
同一ホスト上のDockerコンテナは、コンテナ起動時にプライベートアドレスが自動的に割り振られるので、コンテナ同士で通信するためには、「リンク機能」を使う。コンテナを起動するときに、通信したいコンテナの名前を指定してリンクすると、リンク先の情報が環境変数と/etc/hostsに反映されるため、コンテナ同士が直接通信できるようになる。
ただし、リンク機能を使った通信は同一のホスト上、つまり仮想ブリッジdocker0に接続されたコンテナ同士のみで可能。

## Dockerコンテナと外部ネットワークの通信
Dockerコンテナと外部ネットワークの通信に、Dockerでは、Linuxのiptablesを使用したNAPTの機能を使って接続する。たとえば、コンテナの起動時に、コンテナ内のWebサーバが使用する80番ポートを、ホストOSの8080番ポートに転送するように設定する。すると、外部ネットワークからホストOSの8080番ポートにアクセスすると、コンテナ内の80番ポートにつながる。

## Windowsへのインストール
DockerはLinux上で動作する。Windows環境で実行するには、まずWindows上に仮想環境を構築し、そこれLinuxサーバを動作させる必要がある。
**Windows7と8.1時点**では、「Docker ToolBox」を使用した以下の構成。

インストールするには、PCのBIOS設定でCPUの仮想化支援機能を有効にする。
**Windows10では、**Windows10 Professionalであれば、**Hyper-V**上で動作する「[Docker Desktop](https://www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop)」を使用できる。[WSL](https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/Windows_Subsystem_for_Linux)により、従来の仮想マシンまたはデュアルブート セットアップのオーバーヘッドなしで、Docker環境が利用できる。


😀Hyper-Vは既にレガシーとなり、パフォーマンスが向上した[**WSL 2**](https://matsuand.github.io/docs.docker.jp.onthefly/docker-for-windows/wsl/)に置き換わっている。
# Dockerイメージの操作
## Docker Hub
Docker Hubは、GitHubやBitbucketなどのソースコード管理ツールと連携してコードをビルドする機能や、PaaSサービスであるAWS Elastic BeanstalkやGoogle Compute Engineなどと連携してアプリケーションをデプロイする機能、実行可能なアプリケーションのイメージを管理する機能などを備えたDocker公式のリポジトリサービス。
[https://hub.docker.com/](https://hub.docker.com/)
### ※以降、Dockerコマンドのヘルプより
## イメージのダウンロード(docker pull)
```
Usage: docker pull [OPTIONS] NAME[:TAG|@DIGEST]
Pull an image or a repository from a registry
```
```
Options:
-a, --all-tags Download all tagged images in the repository
--disable-content-trust Skip image verification (default true)
--platform string Set platform if server is multi-platform
capable
-q, --quiet Suppress verbose output
```
タグ名を省略すると、最新バージョン(latest)を取得する。
## イメージの一覧取得(docker images)
```
Usage: docker images [OPTIONS] [REPOSITORY[:TAG]]
List images
```
```
Options:
-a, --all Show all images (default hides intermediate images)
--digests Show digests
-f, --filter filter Filter output based on conditions provided
--format string Pretty-print images using a Go template
--no-trunc Don't truncate output
-q, --quiet Only show numeric IDs
```
## イメージの詳細確認(docker inspect)
```
Usage: docker inspect [OPTIONS] NAME|ID [NAME|ID...]
Return low-level information on Docker objects
```
```
Options:
-f, --format string Format the output using the given Go template
-s, --size Display total file sizes if the type is container
--type string Return JSON for specified type
```
## イメージのタグ設定(docker tag)
```
Usage: docker tag SOURCE_IMAGE[:TAG] TARGET_IMAGE[:TAG]
Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE
```
## イメージの検索(docker search)
```
Usage: docker search [OPTIONS] TERM
Search the Docker Hub for images
```
```
Options:
-f, --filter filter Filter output based on conditions provided
--format string Pretty-print search using a Go template
--limit int Max number of search results (default 25)
--no-trunc Don't truncate output
```
## イメージの削除(docker rmi)
```
Usage: docker rmi [OPTIONS] IMAGE [IMAGE...]
Remove one or more images
```
```
Options:
-f, --force Force removal of the image
--no-prune Do not delete untagged parents
```
## Docker Hubへのログイン(docker login)
```
Usage: docker login [OPTIONS] [SERVER]
Log in to a Docker registry.
If no server is specified, the default is defined by the daemon.
```
```
Options:
-p, --password string Password
--password-stdin Take the password from stdin
-u, --username string Username
```
## イメージのアップロード(docker push)
```
Usage: docker push [OPTIONS] NAME[:TAG]
Push an image or a repository to a registry
```
```
Options:
--disable-content-trust Skip image signing (default true)
```
## Docker Hubからのログアウト(docker logout)
```
Usage: docker logout [SERVER]
Log out from a Docker registry.
If no server is specified, the default is defined by the daemon.
```
# Dockerコンテナの生成/起動/停止
## Dockerコンテナのライフサイクル

## コンテナの生成/起動(docker run)
```
Usage: docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARG...]
Run a command in a new container
```
```
Options:
--add-host list Add a custom host-to-IP mapping
(host:ip)
-a, --attach list Attach to STDIN, STDOUT or STDERR
--blkio-weight uint16 Block IO (relative weight),
between 10 and 1000, or 0 to
disable (default 0)
--blkio-weight-device list Block IO weight (relative device
weight) (default [])
--cap-add list Add Linux capabilities
--cap-drop list Drop Linux capabilities
--cgroup-parent string Optional parent cgroup for the
container
--cidfile string Write the container ID to the file
--cpu-period int Limit CPU CFS (Completely Fair
Scheduler) period
--cpu-quota int Limit CPU CFS (Completely Fair
Scheduler) quota
--cpu-rt-period int Limit CPU real-time period in
microseconds
--cpu-rt-runtime int Limit CPU real-time runtime in
microseconds
-c, --cpu-shares int CPU shares (relative weight)
--cpus decimal Number of CPUs
--cpuset-cpus string CPUs in which to allow execution
(0-3, 0,1)
--cpuset-mems string MEMs in which to allow execution
(0-3, 0,1)
-d, --detach Run container in background and
print container ID
--detach-keys string Override the key sequence for
detaching a container
--device list Add a host device to the container
--device-cgroup-rule list Add a rule to the cgroup allowed
devices list
--device-read-bps list Limit read rate (bytes per second)
from a device (default [])
--device-read-iops list Limit read rate (IO per second)
from a device (default [])
--device-write-bps list Limit write rate (bytes per
second) to a device (default [])
--device-write-iops list Limit write rate (IO per second)
to a device (default [])
--disable-content-trust Skip image verification (default true)
--dns list Set custom DNS servers
--dns-option list Set DNS options
--dns-search list Set custom DNS search domains
--domainname string Container NIS domain name
--entrypoint string Overwrite the default ENTRYPOINT
of the image
-e, --env list Set environment variables
--env-file list Read in a file of environment variables
--expose list Expose a port or a range of ports
--gpus gpu-request GPU devices to add to the
container ('all' to pass all GPUs)
--group-add list Add additional groups to join
--health-cmd string Command to run to check health
--health-interval duration Time between running the check
(ms|s|m|h) (default 0s)
--health-retries int Consecutive failures needed to
report unhealthy
--health-start-period duration Start period for the container to
initialize before starting
health-retries countdown
(ms|s|m|h) (default 0s)
--health-timeout duration Maximum time to allow one check to
run (ms|s|m|h) (default 0s)
--help Print usage
-h, --hostname string Container host name
--init Run an init inside the container
that forwards signals and reaps
processes
-i, --interactive Keep STDIN open even if not attached
--ip string IPv4 address (e.g., 172.30.100.104)
--ip6 string IPv6 address (e.g., 2001:db8::33)
--ipc string IPC mode to use
--isolation string Container isolation technology
--kernel-memory bytes Kernel memory limit
-l, --label list Set meta data on a container
--label-file list Read in a line delimited file of labels
--link list Add link to another container
--link-local-ip list Container IPv4/IPv6 link-local
addresses
--log-driver string Logging driver for the container
--log-opt list Log driver options
--mac-address string Container MAC address (e.g.,
92:d0:c6:0a:29:33)
-m, --memory bytes Memory limit
--memory-reservation bytes Memory soft limit
--memory-swap bytes Swap limit equal to memory plus
swap: '-1' to enable unlimited swap
--memory-swappiness int Tune container memory swappiness
(0 to 100) (default -1)
--mount mount Attach a filesystem mount to the
container
--name string Assign a name to the container
--network network Connect a container to a network
--network-alias list Add network-scoped alias for the
container
--no-healthcheck Disable any container-specified
HEALTHCHECK
--oom-kill-disable Disable OOM Killer
--oom-score-adj int Tune host's OOM preferences (-1000
to 1000)
--pid string PID namespace to use
--pids-limit int Tune container pids limit (set -1
for unlimited)
--platform string Set platform if server is
multi-platform capable
--privileged Give extended privileges to this
container
-p, --publish list Publish a container's port(s) to
the host
-P, --publish-all Publish all exposed ports to
random ports
--read-only Mount the container's root
filesystem as read only
--restart string Restart policy to apply when a
container exits (default "no")
--rm Automatically remove the container
when it exits
--runtime string Runtime to use for this container
--security-opt list Security Options
--shm-size bytes Size of /dev/shm
--sig-proxy Proxy received signals to the
process (default true)
--stop-signal string Signal to stop a container
(default "15")
--stop-timeout int Timeout (in seconds) to stop a
container
--storage-opt list Storage driver options for the
container
--sysctl map Sysctl options (default map[])
--tmpfs list Mount a tmpfs directory
-t, --tty Allocate a pseudo-TTY
--ulimit ulimit Ulimit options (default [])
-u, --user string Username or UID (format:
[:])
--userns string User namespace to use
--uts string UTS namespace to use
-v, --volume list Bind mount a volume
--volume-driver string Optional volume driver for the
container
--volumes-from list Mount volumes from the specified
container(s)
-w, --workdir string Working directory inside the container
```
## 稼働コンテナの一覧表示(docker ps)
```
Usage: docker ps [OPTIONS]
List containers
```
```
Options:
-a, --all Show all containers (default shows just running)
-f, --filter filter Filter output based on conditions provided
--format string Pretty-print containers using a Go template
-n, --last int Show n last created containers (includes all
states) (default -1)
-l, --latest Show the latest created container (includes all
states)
--no-trunc Don't truncate output
-q, --quiet Only display numeric IDs
-s, --size Display total file sizes
```
## 稼働コンテナの一覧表示(docker stats)
```
Usage: docker stats [OPTIONS] [CONTAINER...]
Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics
```
```
Options:
-a, --all Show all containers (default shows just running)
--format string Pretty-print images using a Go template
--no-stream Disable streaming stats and only pull the first result
--no-trunc Do not truncate output
```
## コンテナの起動(docker start)
```
Usage: docker start [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [CONTAINER...]
Start one or more stopped containers
```
```
Options:
-a, --attach Attach STDOUT/STDERR and forward signals
--checkpoint string Restore from this checkpoint
--checkpoint-dir string Use a custom checkpoint storage directory
--detach-keys string Override the key sequence for detaching a
container
-i, --interactive Attach container's STDIN
```
## コンテナの停止(docker stop)
```
Usage: docker stop [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [CONTAINER...]
Stop one or more running containers
```
```
Options:
-t, --time int Seconds to wait for stop before killing it (default 10)
```
## コンテナの再起動(docker restart)
```
Usage: docker restart [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [CONTAINER...]
Restart one or more containers
```
```
Options:
-t, --time int Seconds to wait for stop before killing the container
(default 10)
```
## コンテナの削除(docker rm)
```
Usage: docker rm [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [CONTAINER...]
Remove one or more containers
```
```
Options:
-f, --force Force the removal of a running container (uses SIGKILL)
-l, --link Remove the specified link
-v, --volumes Remove anonymous volumes associated with the container
```
## コンテナの中断/再開(docker pause/docker unpause)
```
Usage: docker pause CONTAINER [CONTAINER...]
Pause all processes within one or more containers
```
```
Usage: docker unpause CONTAINER [CONTAINER...]
Unpause all processes within one or more containers
```
# 稼働しているDockerコンテナの操作
## 稼働コンテナへの接続(docker attach)
```
Usage: docker attach [OPTIONS] CONTAINER
Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container
```
```
Options:
--detach-keys string Override the key sequence for detaching a
container
--no-stdin Do not attach STDIN
--sig-proxy Proxy all received signals to the process
(default true)
```
## 稼働コンテナでプロセス実行(docker exec)
```
Usage: docker exec [OPTIONS] CONTAINER COMMAND [ARG...]
Run a command in a running container
```
```
Options:
-d, --detach Detached mode: run command in the background
--detach-keys string Override the key sequence for detaching a
container
-e, --env list Set environment variables
-i, --interactive Keep STDIN open even if not attached
--privileged Give extended privileges to the command
-t, --tty Allocate a pseudo-TTY
-u, --user string Username or UID (format:
[:])
-w, --workdir string Working directory inside the container
```
## 稼働コンテナのプロセス確認(docker top)
```
Usage: docker top CONTAINER [ps OPTIONS]
Display the running processes of a container
```
## 稼働コンテナのポート転送確認(docker port)
```
Usage: docker port CONTAINER [PRIVATE_PORT[/PROTO]]
List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container
```
## コンテナの名前変更(docker rename)
```
Usage: docker rename CONTAINER NEW_NAME
Rename a container
```
## コンテナ内のファイルをコピー(docker cp)
```
Usage: docker cp [OPTIONS] CONTAINER:SRC_PATH DEST_PATH|-
docker cp [OPTIONS] SRC_PATH|- CONTAINER:DEST_PATH
Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem
Use '-' as the source to read a tar archive from stdin
and extract it to a directory destination in a container.
Use '-' as the destination to stream a tar archive of a
container source to stdout.
```
```
Options:
-a, --archive Archive mode (copy all uid/gid information)
-L, --follow-link Always follow symbol link in SRC_PATH
```
## コンテナ操作の差分確認(docker diff)
```
Usage: docker diff CONTAINER
Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem
```
# Dockerの情報確認
## Dockerのバージョン確認(docker version)
```
Usage:
docker version [flags]
Flags:
-f, --format string Format the output. Values: [pretty | json]. (Default: pretty)
-h, --help Help for version
--kubeconfig string Kubernetes config file
```
## Dockerの実行環境確認(docker info)
```
Usage: docker info [OPTIONS]
Display system-wide information
```
```
Options:
-f, --format string Format the output using the given Go template
```
# コンテナからイメージの作成
## コンテナからイメージ作成(docker commit)
```
Usage: docker commit [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [REPOSITORY[:TAG]]
Create a new image from a container's changes
```
```
Options:
-a, --author string Author (e.g., "John Hannibal Smith
<hannibal@a-team.com>")
-c, --change list Apply Dockerfile instruction to the created image
-m, --message string Commit message
-p, --pause Pause container during commit (default true)
```
## コンテナをtarファイル出力(docker export)
```
Usage: docker export [OPTIONS] CONTAINER
Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive
```
```
Options:
-o, --output string Write to a file, instead of STDOUT
```
```
Example:
$ docker export webapp > latest.tar
```
## tarファイルからイメージ作成(docker import)
```
Usage: docker import [OPTIONS] file|URL|- [REPOSITORY[:TAG]]
Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image
```
```
Options:
-c, --change list Apply Dockerfile instruction to the created image
-m, --message string Set commit message for imported image
--platform string Set platform if server is multi-platform capable
```
```
Example:
$ cat latest.tar | docker import - webap:1.0
```
## イメージの保存(docker save)
```
Usage: docker save [OPTIONS] IMAGE [IMAGE...]
Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default)
```
```
Options:
-o, --output string Write to a file, instead of STDOUT
```
```
Example:
$ docker save -o export.tar webap
```
## イメージの読み込み(docker load)
```
Usage: docker load [OPTIONS]
Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN
```
```
Options:
-i, --input string Read from tar archive file, instead of STDIN
-q, --quiet Suppress the load output
```
```
Example:
$ docker load -i export.tar
```
# Dockerfileファイルの基本
## Dockerfileの基本構成
|命令|説明|
|----|----|
|FROM|ベースイメージの指定|
|MAINTAINER|Dockerfileの作成者情報|
|RUN|コマンド実行|
|CMD|デーモン実行|
|LABEL|ラベルの設定|
|EXPOSE|ポートのエクスポート|
|ENV|環境変数の設定|
|ADD|ファイル/ディレクトリの追加|
|COPY|ファイルのコピー|
|VOLUME|ボリュームのマウント|
|ENTRYPOINT|デーモン実行|
|USER|ユーザの指定|
|WORKDIR|作業ディレクトリの指定|
|ONBUILD|ビルド完了後に実行される命令|
[Dockerfile を書くベストプラクティス](https://docs.docker.jp/develop/develop-images/dockerfile_best-practices.html)
## DockerfileからDockerイメージの作成(docker build)
```
Usage: docker build [OPTIONS] PATH | URL | -
Build an image from a Dockerfile
```
```
Options:
--add-host list Add a custom host-to-IP mapping (host:ip)
--build-arg list Set build-time variables
--cache-from strings Images to consider as cache sources
--disable-content-trust Skip image verification (default true)
-f, --file string Name of the Dockerfile (Default is
'PATH/Dockerfile')
--iidfile string Write the image ID to the file
--isolation string Container isolation technology
--label list Set metadata for an image
--network string Set the networking mode for the RUN
instructions during build (default "default")
--no-cache Do not use cache when building the image
-o, --output stringArray Output destination (format:
type=local,dest=path)
--platform string Set platform if server is multi-platform
capable
--progress string Set type of progress output (auto, plain,
tty). Use plain to show container output
(default "auto")
--pull Always attempt to pull a newer version of
the image
-q, --quiet Suppress the build output and print image
ID on success
--secret stringArray Secret file to expose to the build (only
if BuildKit enabled):
id=mysecret,src=/local/secret
--ssh stringArray SSH agent socket or keys to expose to the
build (only if BuildKit enabled) (format:
default|[=|[,]])
-t, --tag list Name and optionally a tag in the
'name:tag' format
--target string Set the target build stage to build.
```
```
Example:
$ docker build -t sample:1.0 .
$ docker build - < Dockerfile
$ docker build - < docker.tar.gz
```
# プライベートレジストリの構築/管理
## Dockerレジストリの構築
```
$ docker pull registry:2
$ docker run -d --name registry -p 5000:5000 registry:2
```
この場合、ホストマシンの「/tmp/registry-dev」配下にデータが保存される。
Amazon S3を使ったプライベートレジストリの起動
```
$ docker run -d \
--name registry \
-p 5000:5000 \
-e REGISTRY_STORAGE=s3 \
-e REGISTRY_STORAGE_S3_ACCESSKEY=xxxx \
-e REGISTRY_STORAGE_S3_SECRETKEY=yyyy \
-e REGISTRY_STORAGE_S3_BUCKET=zzzz \
-e REGISTRY_STORAGE_S3_REGION=ap-northeast-1 \
-e REGISTRY_STORAGE_S3_ROOTDIRECTORY=/tmp \
registry:2.0
```
## イメージのアップロード
プライベートレジストリにアップロードするには、次のルールでイメージにタグを付ける。
```
docker tag [ローカルのイメージ名] [DockerレジストリのIPアドレスまたはホスト名:ポート番号]/[イメージ名]
```
```
Example:
$ docker tag testweb localhost:5000/httpd
$ docker push localhost:5000/httpd
```
## プライベートレジストリの使用例
```
# 自動的に起動するよう再起動ポリシーに「--restart always」を指定
docker run -d -p 5000:5000 --restart always --name registry registry:2
# イメージのタグ設定
docker tag sourceimage localhost:5000/targetimage
# イメージのアップロード
docker push localhost:5000/targetimage
# プライベートリポジトリのカタログ取得
curl http://localhost:5000/v2/_catalog
# 不要になったイメージを削除
docker rmi sourceimage localhost:5000/targetimage
```
[再起動ポリシー](https://docs.docker.jp/config/container/start-containers-automatically.html)
## その他開発支援のための公式イメージ
|ツール|説明|DockerHubサイト|
|----|----|----|
|Jenkins|継続的インテグレーションツール|[https://hub.docker.com/_/jenkins/](https://hub.docker.com/_/jenkins/)|
|Redmine|統合プロジェクト管理ツール|[https://hub.docker.com/_/redmine/](https://hub.docker.com/_/redmine/)|
|Maven|Java用プロジェクト管理ツール|[https://hub.docker.com/_/maven/](https://hub.docker.com/_/maven/)|
|SonarQube|統合品質管理ツール|[https://hub.docker.com/_/sonarqube/](https://hub.docker.com/_/sonarqube/)|
|Rocket.Chat|チャットツール|[https://hub.docker.com/_/rocket.chat/](https://hub.docker.com/_/rocket.chat/)|
# 複数コンテナの一元管理(Docker Compose)
## 構成ファイル(docker-compose.yml)の構文
[Compose Specification](https://docs.docker.jp/compose/compose-file/index.html)
構成例:
```
services:
myapp-httpd:
container_name: test-httpd-container
build:
context: ./middleware/httpd
dockerfile: Dockerfile
ports:
- 8080:80
myapp-cf:
container_name: test-cf-container
image: localhost:5000/test-cf-image:1.2
ports:
- 8501:8500
- 5005:5005
volumes:
- ./html:/app
- ./CustomTags:/opt/coldfusion/cfusion/CustomTags/custom
environment:
- acceptEULA=YES
- password=hoge
- language=ja
- installModules=postgresql
- setupScript=setupColdFusion.cfm
- TZ=Asia/Tokyo
myapp-db:
container_name: test-db-container
image: postgres:latest
ports:
- 5435:5432
volumes:
- ./middleware/postgres/initdb:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d:ro
environment:
POSTGRES_HOST_AUTH_METHOD: trust
POSTGRES_DB: testdb
POSTGRES_USER: hoge
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: hoge
TZ: Asia/Tokyo
```
## Compose の ネットワーク機能
> デフォルトで Compose はアプリに対して1つの ネットワーク を作成します。サービス用の各コンテナはデフォルトのネットワークに接続し、そのネットワーク上で他のコンテナと相互に「接続可能(reachable)」になります。そして、コンテナ名と同じホスト名として、お互いが「発見可能(discoverable)」になります。
[Compose の ネットワーク機能](https://docs.docker.jp/compose/networking.html)
# Docker Composeコマンド
## Docker Composeのコマンド
```
Usage: docker compose [OPTIONS] COMMAND
Docker Compose
```
```
Options:
--ansi string Control when to print ANSI control
characters ("never"|"always"|"auto")
(default "auto")
--compatibility Run compose in backward compatibility mode
--env-file string Specify an alternate environment file.
-f, --file stringArray Compose configuration files
--parallel int Control max parallelism, -1 for
unlimited (default -1)
--profile stringArray Specify a profile to enable
--project-directory string Specify an alternate working directory
(default: the path of the, first
specified, Compose file)
-p, --project-name string Project name
```
```
Commands:
build Build or rebuild services
convert Converts the compose file to platform's canonical format
cp Copy files/folders between a service container and the local filesystem
create Creates containers for a service.
down Stop and remove containers, networks
events Receive real time events from containers.
exec Execute a command in a running container.
images List images used by the created containers
kill Force stop service containers.
logs View output from containers
ls List running compose projects
pause Pause services
port Print the public port for a port binding.
ps List containers
pull Pull service images
push Push service images
restart Restart service containers
rm Removes stopped service containers
run Run a one-off command on a service.
start Start services
stop Stop services
top Display the running processes
unpause Unpause services
up Create and start containers
version Show the Docker Compose version information
Run 'docker compose COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.
```














0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿